آقاي ساسان سلام
اگر بيماري در حال پيشرفت باشد،نقاط جديد بدن كه تازه دارند رنگدانه از دست مي دهند ولي هنوز روند پيشرفت ادامه دارد،خيلي سفيد نيستند،در خصوص سوال دوم،چنين آمپول و درماني وجود ندارد،بهترين درمان براي شما نور درماني هست .
• In the early I 950s, physicians began using systemically administered cortisol to treat inflammatory dermatoses.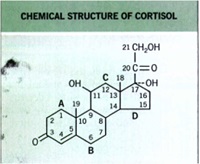
• Unfortunately, corticosteroids with a ketone group at the C 11 position (e.g., cortisone) must be reduced to their corresponding
11-hydroxyl analogs (e.g., hydrocortisone) to be active-a reduction that does not occur effectively in the skin.
Thus, early attempts to use topical
cortisone failed until 1952, when Sulzberger and
Witten successfully treated eczematous dermatitis with topical hydrocortisone.
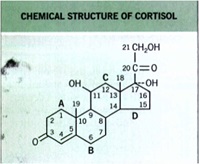
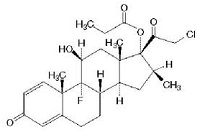
Structure of TCS Molecules
Basic
cyclopentanophenanthrene nucleus .. three 6-carbon rings (A, B, C) + a single 5-carbon ring (D)
• potency is significantly increased by modifications at:
• C-6a or C-9a Fluorination
• C-21 Halogenation
• C-17. C-21 Esterification
• Double bond between C-1 and C-2 on ring A
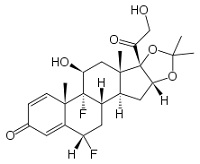
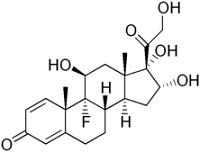
• Q1. which factors have affect the clinical potency of a TCS preparation?
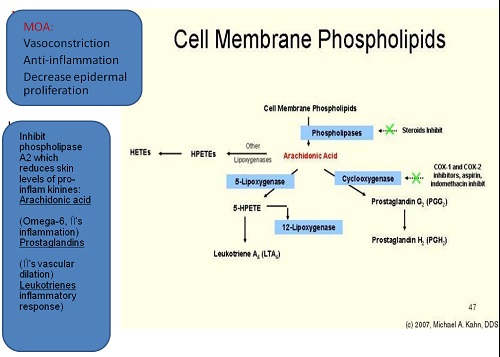
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics and resultant clinical potency of a TCS preparation depend on three interrelated factors:
(1) the structure of the corticosteroid molecule
(2) the vehicle, and
(3) the skin onto which the TCS is applied.
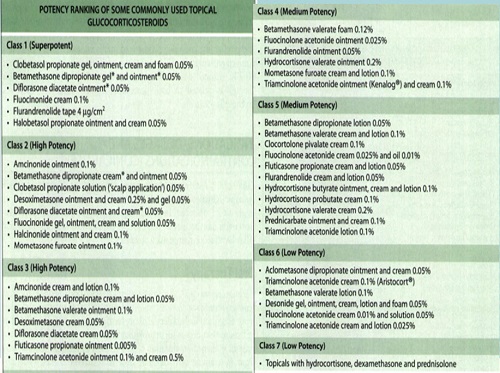
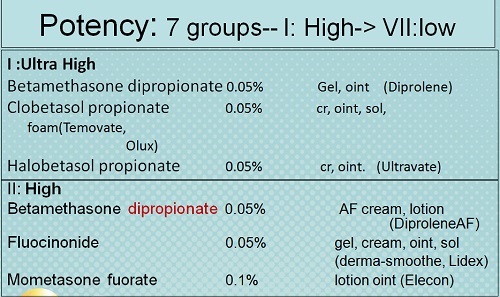
Potency
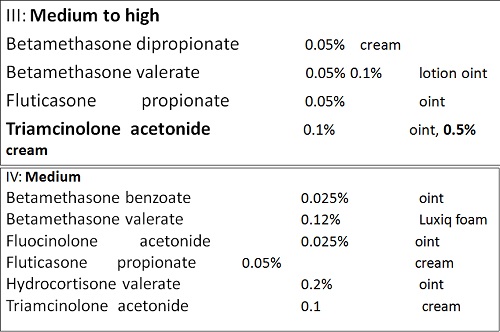
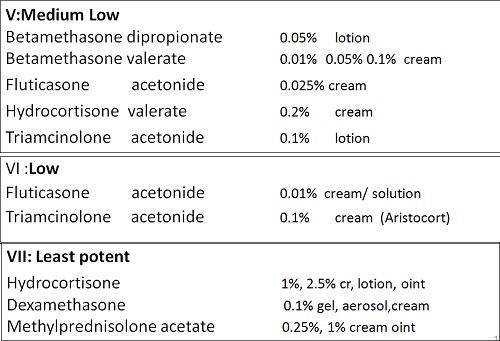
• There are seven groups of topical steroid potency, ranging from ultra high potency (group I) to low potency (group VII).
• Fluorinated topical steroids are generally more potent than others
– IE: triamcinolone acetonide (contains fluoride ion) is 100x more potent than nonfluorinated HC
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics and resultant clinical potency of a TCS preparation depend on three interrelated factors:
(1) the structure of the corticosteroid molecule
(2) the vehicle
(3) the skin onto which the TCS is applied.
• Q2. What’s the best steroid’s vehicle in a px with an acute vesicular or weeping rashes?
Ointments
• Most effective
• Ointment have oily/greasy base (ie:petroleum jelly)
• Greasy texture persists on the skin surface
• Translucent
• Best lubrication, penetration
• Best for dry or thick, hyperkeratotic lesions
• Not recommended for areas where skin touches skin or acute vesicular or weeping rashes
• poor pt satisfaction / compliance
Creams
• most often prescribed
• water suspended in oil
• white color/ less greasy/ vanish into the skin
• good lubricating/ emollient qualities
• generally less potent than ointments of the same medication,
• often contain preservatives (cause irritation, stinging, allergic reaction)
• USE:
– most skin areas, useful where skin touches skin (groin, rectal area, armpits )
– acute exudative inflammation, drying effect / repeated use
Lotions and gels
• Solution or lotion : bases contain water, alcohol, other chemicals
• Clear or milky appearance
• least greasy & occlusive
• drying effect on an oozing lesion
• useful for use on the scalp , no residue
• can cause stinging and drying
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics and resultant clinical potency of a TCS preparation depend on three interrelated factors:
(1) the structure of the corticosteroid molecule
(2) the vehicle
(3) the skin onto which the TCS is applied.
• Q3. In which location of the body has highest steroidal absorption ?
• Face
• mucous membranes
• scrotum
• eyelids
• torso
• extremities
Skin absorption of topical steroids
• Forearm absorbs 1%
• Armpit absorbs 4%
• Face absorbs 7%
• Eyelids and genitals absorb 30-40%
• Palm absorbs 0.1%
• Sole absorbs 0.05%
• Penetration of the applied drug correlates inversely
with the thickness of the stratum corneum.
• Absorption: Thin to thick stratum corneum:
mucous membranes -> scrotum-> eyelids-> face-> torso-> extremities-> palm,soles, elbows, knees
• Penetration increases with inflamed or diseased Skin
• Increases with increased hydration of the stratum corneum, relative humidity, and temperature.
• The stratum corneum may also act as a reservoir
for TCS for up to 5 days; this retention is TCS
concentration- and formulation-dependent.
Occlusion
• Occlusion: determines penetration
• Occlusion: ’s hydration-> ’s penetration-> ’s potency
• Intertriginous: touching skin acts like occlusive dssg (axillae, inguinal)
• Create Occlusion: non-breathing saran wrap, held by tape, sock, Ace; leave on all noc
– ie plastic shower cap; cordran tape rubber gloves, baggies, sauna suits.
Q4. What is the procedure for assessing potency of topical corticosteroid molecules and how does this assay?


assay of choice because it usually correlates well with clinical efficacy
and is reproducible.
The actual vasoconstriction assay usually involves the following:
• (I) Preparing the test corticosteroid in 95% alcohol;
• (2) Applying it to the volar surface of a normal volunteer's forearm
• (3) Allowing the alcohol to evaporate, then covering the test area with an occlusive dressing for 16 hours
• (4) Washing off the area;
• (5) Assessing vasoconstriction (0 = none, 1 = mild,
2 = moderate, and 3 = intense) 2 hours later on a blind basis by an experienced investigator; and
• (6) Using statistical analysis, mostly with the Wilcoxson rank sum test, based on the sum of signed ranks of difference.
Q5. What are the most important factors in choosing a specific TCS product?
Choosing a TCS Preparation
The clinician must make decisions regarding the following
• (I) TCS potency
• (2) vehicle choice
• (3) brand name versus generic products
• (4) price and cost-effectiveness considerations
• (5) proper amount to dispense.
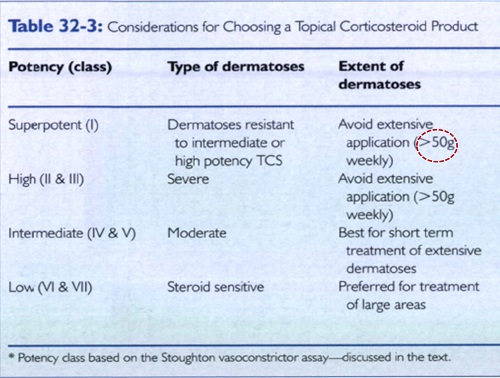
TCS potency selection
• Patient's age
• diseasee type
• severity
• extent
• location,
• and expected duration of the dermatosis.

Choosing a TCS Preparation
• (I) TCS potency
• (2) vehicle choice
The most important factors in selecting a vehicle
• location of use
• Potential for irritation
• past allergic reactions.
Q5.what’s the best vehicle for a dermatosis located in naturally occluded area?
Q6. With highest potential for irritation?
Choosing a TCS Preparation
• (I) TCS potency
• (2) vehicle choice
• (3) brand name versus generic products
• (4) price and cost-effectiveness considerations (5) proper amount to dispense.
• Q7. what’s the best way for ordering the proper amounts of TCS?
Amount of application
A fingertip unit (FTU) is the amount of ointment expressed from a tube with a 5-mm diameter nozzle, applied from the distal skin crease to the tip of the palmar aspect of the index finger.
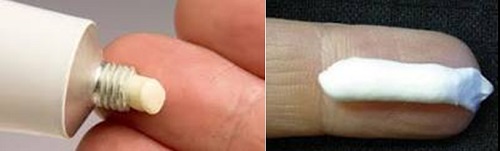
Q8. what’s the proper amounts for each parts of body based on FTU?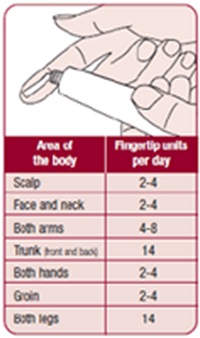
• One hand: apply one fingertip unit
• One arm: apply three fingertip units
• One foot: apply two fingertip units
• One leg: apply six fingertip units
• Face and neck: apply 2.5 fingertip units
• Trunk, front & back: 14 fingertip units
• Entire body: about 40 units
Q9. What’s your strategy about proper amount of TCS in Children?
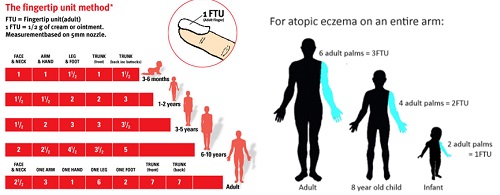
Q10. How many times you order TCS to your Px?
Frequency of Administration
• QD or BID application
• No improved result for more frequent administration
• Chronic application can induce tachyphylaxis (tolerance)
• Max 3wks for ultra-high-potency steroids
Q11. What is the rebound phenomenone?
Q12. What are several of the most important factors leading to the development of the addiction/rebound syndrome?
Addiction/Rebound Syndrome
The addiction/rebound syndrome is characterized
by initial improvement with a TCS,
followed
by lack of response after continued application,
Followed
by a flare after TCS withdrawal.
Q13. what’s the most common location for this phenomenone?
Q14. Take a well-known example
The syndrome frequently occurs on 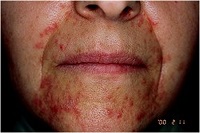
• facial
• Genital
• perianal skin
with involvement on the face being the most common location.
Q15. How does tachyphylaxis occur with TCS therapy, and which TCS potency groups are at particular risk for this complication of therapy?
Tachyphylaxis
Tachyphylaxis is the acute development of tolerance to the action of a drug after repeated doses.
Loss of clinical effect is a well-known problem with
chronic TCS application, particularly with higher
potency TCS.
• Q16. What’s the best strategy to avoid tachyphylaxis?
A proven regimen to prevent tachyphylaxis does not
Twice daily application for 2 weeks on, then I week off, is recommended because it seems easier for patients to remember.

Q 17. What are several of the most important risk factors for systemic adverse effects from TCS therapy?

Q18. What’s the minimm amount of TCS that could be enconterd the systemic side effects?
Normal and psoriatic or eczematous adult
volunteers applying over 50g of 0.05% clobetasol
propionate (Dermovate) cream or ointment weekly
showed either depressed 9 AM serum cortisol levels
or decreased peak insulin stress tests by 1 week.
Over l00g caused profound AM cortisol suppression.
Atrophy of the epidermis may be seen within the first 7 days of daily superpotent TCS application under
and within 2 weeks of daily use of less potent TCS or superpotent TCS without occlusion.
Risk factors for atrophy:
• corticosteroid potency
• occlusion
• infancy/childhood
• location of TCS use(face, neck, axilla, groin, upper inner thighs, pretibial)
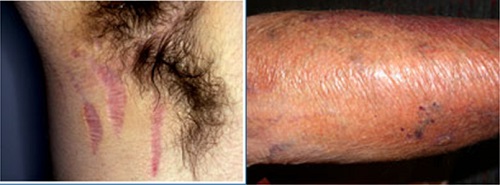
Q19. How long the steroidal atrophy usually last?
• Atrophy of the fat and muscle in the diaper area has occurred with fluorinated TCS.
• Most signs of cutaneous atrophy resolve by 1 to 4 weeks after discontinuation of the TCS; however, striae are permanent.
Continuous long-term treatment with a TCS preparation near puberty should also be avoided because growth suppression may cause premature epiphyseal closure before catch-up growth can occur.
Q20. How are some of the ocular complications from TCS applied in a periorbital distribution
Although reports of ocular adverse effects from TCS applied to the eyelid skin are rare studies with ophthalmologic preparations indicate that prolonged use on conjunctival tissue can lead to
• glaucoma, cataracts, decreased healing of traumatic
• ulcers, exacerbation of herpetic ulcers, and increased
• susceptibility to fungal and bacterial infections.
Glaucoma and blindness have occurred after
12 years intermittent use of 1% hydrocortisone creamfor periorbital involvement of atopic dermatitis.
Vehicle-Related Adverse Effects
The vehicle of a TCS preparation can potentiate the adverse effects of the TCS or cause local adverse effects of its own.
Components of the vehicle can cause
itching,
Burning
stinging
Urticaria
irritant contact dermatitis.
• Frequent causes of stinging include
benzoic acid, cinnamic acid compound, lactic acid, emulsifiers, formaldehyde, and sorbic acid
Propylene glycol, alcohol, and acetone can be very irritating.
TCS preparations can contain agents that cause
non immunologic contact urticaria including
acetic acid
alcohols
balsam of Peru
benzoic acid
cinnamic acid, formaldehyde, sodium benzoate, and sorbic acid.
Immunologic causes include
• acrylic monomer
• alcohols
• Ammonia
• benzoic acid
• benzophenone,
• diethyl toluamide
• formaldehyde
• henna,
• Menthol
• parabens
• polyethylene glycol, polysorbate60
• salicylic acid
• sodium sulfide
Very occlusive vehicles can cause
• folliculitis
• miliaria
• exacerbation of acne and rosacea.
• Vehicle ingredients can be the cause of ACD to a TCS preparation.
Q21. What the most predisposing factors for TCS allergy?
• Currently, more than 50 different TCS products have been reported to cause positive patch test reactions.
• prevalence of ACD due to TCS ranges from 0.2% to 4.8%.
Predisposing factors for TCS allergy are a
• history of numerous positive patch tests to non-TCS allergens
• treatment-resistant eczema
• leg ulcers
• stasis dermatitis
• perineal dermatitis
• chronic actinic dermatitis.
• ACD to a TCS product may involve allergy to
either a component of the vehicle or the actual TCS molecule.
• However, it may also be due to irritation from or allergy to other components of the preparation such as preservatives. Lanolin, ethylenediamine, quaternium-15 and the antibacterial agent neomycin, are all known to be potent sensitisers.
Q22.What are the reactions in cases of corticosteroid allergy?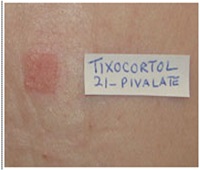
• Allergic sensitivity to topical corticosteroids is usually only picked up when an eczematous dermatitis being treated by a topical corticosteroid fails to respond to treatment or worsens.
• Positive patch test reactions to budesonide and tixocortol-21-pivalate hydrocortisone-17 -butyrate, are a good indicator of corticosteroid allergy.
• These 2 corticosteroids are often included in the standard panel.
• Further testing with other corticosteroids should be done if these 2 indicators are positive.
Cross reactions
When patch tests show allergy to a specific topical steroid, it is likely that the patient will also be allergic to others.
• Budesonide may result in allergy to fluocinolone, triamcinolone, hydrocortisone-17-butyrate, methylprednisolone aceponate and prednicarbate.
• Tixocortol-21-pivalate may result in allergy to hydrocortisone (acetate), prednisolone, diflucortolone, methylprednisolone, hydrocortisone-17-butyrate, methylprednisolone aceponate and prednicarbate.
• Hydrocortisone-17-butyrate allergy may result in allergy to methylprednisolone aceponate, prednicarbate, alclomethasone dipropionate, budesonide and hydrocortisone (acetate).
Treatment of a TCS-induced ACD involves choosing a TCS from a different cross-reactivity group.
Q23. Do you can use TCS in Prgnancy or Lactation?
TCS in Pregnancy and lactation
• In pregnancy, TCS preparations may cause fetal
abnormalities in animals if used in large amounts,
with occlusive dressings, for prolonged periods of
time, or if the more potent agents are used.
• Fetal abnormalities due to TCS have not been documented in human beings.
TCS in lactation
It is not known whether TCS molecules are excreted in breast milk, although no adverse effects on lactation from the use of TCS preparations have been documented in humans.
• TCS products should not be applied to the nipples before nursing.
Q24. Is there any problem if you want to Compound the TCS with another ingredient in one formulation?
Compounding Utilizing TCS
• Compounding TCS with certain
salicylates, tar, antibiotics, and antifungals
may alter the stability or solubility of the corticosteroid or cause contact allergy.
Urea 10% has been shown to cause significant degradation of the TCS in Topicort, Kenalog, and Westcort creams.
No such degradation of TCS occurred with
0.25% menthol
camphor
phenol
2% salicylic acid.
Q25. Is there any contra indication for using TCS?

This document has been edited with the instant web content composer. The online instant HTML editor tools make a great resource that will help you a lot in your work. Save this link or add it to your bookmarks.
آقاي ساسان سلام
اگر بيماري در حال پيشرفت باشد،نقاط جديد بدن كه تازه دارند رنگدانه از دست مي دهند ولي هنوز روند پيشرفت ادامه دارد،خيلي سفيد نيستند،در خصوص سوال دوم،چنين آمپول و درماني وجود ندارد،بهترين درمان براي شما نور درماني هست .
زمان بهترین و ارزشمندترین هدیه ای است كه می توان به كسی ارزانی داشت.هنگامی كه برای كسی وقت می گذاریم، قسمتی از زندگی خود را به او میدهیم كه باز پس گرفته نمی شود . باعث خوشحالی و افتخار من است كه برای عزیزی مثل شما وقت می گذارم و امیدوارم كه با راهنماییهای اساتید این رشته واظهار نظر شما عزیزان این سایت آموزشی پر بارتر گردد.